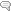Строка 8
 12.09.2008 от
12.09.2008 от  Maxim
Maxim
Фото1:
Самая яркая на данный момент известная звезда - Эта Киля. Её светимость- 4.7 миллионов наших солнц. Второе место - показанная на фотографии звезда Туманности Пиона. Её светимость оценивается в 3.2 миллионов солнц. Эту звезду раскопал “в пыльном и взбешенном интерьере галактики” Спицеровский космический телескоп НАСА в ИК-диапазоне. В видимом диапазоне звезду скрывает пыль.
Peony Nebula Star Settles for Silver Medal
If our galaxy were to host its own version of the Olympics, the title for the brightest known star would go to a massive star called Eta Carina. However, a new runner-up, now the second-brightest star in our galaxy, has been discovered in the galaxy’s dusty and frenzied interior. This image from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope shows the new silver medalist in the central region of our Milky Way.
Dubbed the Peony nebula star, this blazing ball of gas shines with the equivalent light of 3.2 million suns. The reigning champ, Eta Carina, produces the equivalent of 4.7 million suns worth of light. However, astronomers say these estimates are uncertain, and it’s possible that the Peony nebula star could be even brighter than Eta Carina.
If the Peony star is so bright, why doesn’t it stand out more in this view? The answer is dust. This star is located in a very dusty region jam packed with stars. In fact, there could be other super bright stars still hidden deep in the stellar crowd. Spitzer’s infrared eyes allowed it to pierce the dust and assess the Peony nebula star’s true brightness. Likewise, infrared data from the European Southern Observatory’s New Technology Telescope in Chile were integral in calculating the Peony nebula star’s luminosity.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Potsdam Univ.
Фото 2:
Пылевые Облака Туманности Киля, Какие темные формы скрываются в облака пыли Туманности Киля? Эти зловещие образования- фактически молекулярные облака, образования молекулярного газа и пыли, столь плотных, что они стали непрозрачными. В сравнении, однако, эти облака типично намного менее плотны чем атмосфера Земли. Изображенная выше часть самого детального изображения Туманности Киля, когда-либо имеющейся, где темные молекулярные облака являются особенно видными. Вся Туманность Киля охватывает больше чем 300 световых лет.
NGC 3372, известный как Большая Туманность в Киле, является родиной массивных звезд и изменяющейся туманности. Carinae Эты, самая энергичная звезда в туманности, была одной из самых ярких звезд в небе в 1830-ых, и потом исчезла.
Dark Clouds of the Carina Nebula
What dark forms lurk in the mists of the Carina Nebula? These ominous figures are actually molecular clouds, knots of molecular gas and dust so thick they have become opaque. In comparison, however, these clouds are typically much less dense than Earth’s atmosphere.
Pictured above is part of the most detailed image of the Carina Nebula ever taken where dark
molecular clouds are particularly prominent. The entire Carina Nebula spans more than 300 light years and lies about 7,500 light-years away in the constellation of Carina.
NGC 3372, known as the Great Nebula in Carina, is home to massive stars and changing nebula. Eta Carinae, the most energetic star in the nebula, was one of the brightest stars in the sky in the 1830s, but then faded dramatically. Wide-field annotated and zoomable versions of the larger image composite are also available.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, N. Smith (U. California, Berkeley) et al., and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Фото3:
Обзор Феникса. Объединение больше чем 400 изображений, Феникс НАСА, приземлившийся на Марсе рассматривает его среду в самой северной области Красной планеты. Обзор полного круга в приблизительно истинном цвете показывает многоугольное копирование основания в месте посадки, подобном образцам в областях вечной мерзлоты на Земле. Юг находится к вершине. Траншеи, где автоматизированная рука Финикса забирала пробы грунта, видны в более низкой половине изображения. Мачта метеорологии космического корабля, оканчивающаяся анемометром, видна на фоне неба.
Phoenix Looks Around
Combining more than 400 images, NASA’s Phoenix Mars Lander views its surroundings in the Red Planet’s northernmost region.
The full-circle panorama in approximately true color shows the polygonal patterning of ground at the landing area, similar to patterns in permafrost areas on Earth. South is toward the top. Trenches, where Phoenix’s robotic arm has been exposing subsurface material, are visible in the lower half of the image. The spacecraft’s meteorology mast, topped by the telltale wind gauge, extends into the sky portion of the panorama.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/Texas A&M University
Фото4:
Тропический шторм Edouard в Заливе, Это изображение, снятое бортинженером Международной космической станции Greg Chamitoff, показывает Тропический ураган Эдвард, перемещающийся на запад вдоль северного края Мексиканского залива утром понедельник, 4 августа 2008. Согласно Ассошиэйтед Пресс, шторм “поражал побережье Залива Техаса к востоку от Галвестона во вторник с сильными ветрами и льется дождем, но, как ожидали, будет слабеть, поскольку это пробивается внутри страны в течение дня.”
Edouard in the Gulf
This image, taken from aboard the International Space Station flight engineer Greg Chamitoff, is of Tropical Storm Edouard as it moved westward along the northern edge of the Gulf of Mexico on the morning of Monday, Aug. 4, 2008 .
According to the Associated Press, the storm “hit the Texas Gulf coast east of Galveston on Tuesday with strong winds and rain but was expected to weaken as it makes its way inland during the day.”
Рубрики: Далекий космос, Звездообразование, Земля, Марс |